WordPress is the ‘default’ choice of most people looking to start their website. From basic blogging pages to the most advanced sites, the free website builder functions very well for different purposes.
But have you ever wondered, “Where does WordPress store the content of posts and pages of your entire site? And most importantly, how does it process them to the visitors of your webpage?
Beginner WordPress site developers usually don’t have enough information about how their data is stored and processed on WordPress. They simply choose to use the Content Management System for its ease of use, robust systems, and vast availability of plugins and WordPress themes to customize their online page.
However, knowing the practices will help resolve any issues that can potentially occur with the WordPress CMS. And allow you to enhance more focus on the content, SEO, and marketing aspects of the page.
In this beginner’s guide, we will tell you the details of how WordPress manages your data. You will also learn about files that require backup and troubleshooting tips to keep your website running optimally at all times.
So without further ado, let’s get started!
How WordPress Works?
Instead of creating static HTML files for each page of your WordPress site, the CMS uses PHP scripts. Every time a visitor queries for a page, the website builder loads a set of scripts that retrieves the required WordPress files from its specific database.
Besides the database, WordPress also includes:
- A core file that comes with WordPress installation
- Any other file you upload such as media attachments, WordPress plugins, and themes
Where does WordPress Store Posts and Pages?
The wp_posts serves as the main table of contents where WordPress stores all your pages, posts, and revisions. This table also contains any attachments and the navigation menu items that you have included in your webpage.
The database is managed by a software termed as MySQL.
MySQL operates as a web server giving multiple users access simultaneously and enabling them to create databases that store information on your website. It also retrieves the WordPress data when needed.
Ok, So Who Administers MySQL?
PhpMyAdmin, a free web tool/software that deals with MySQL database management and works as the WordPress admin. This software facilitates the following operations with the MySQL database tables:
- Create
- Make Changes
- Drop
- Delete
- Import
- Export
So in the descending order, the major database participating software are:
PhpMyAdmin →→ MySQL →→ wp_posts →→ Pages (Stored)
Why Is PhpMyAdmin Specifically Used As A WordPress Admin for Database?
This software is primarily sourced in a PHP script, which is the core scripting language, and MySQL is the Database that WordPress is written in. PHP lets you create only dynamic web pages.
How To Navigate To The Wp_Posts Table?
Now that you know how WordPress Database management stores your pages and posts – let us guide you to the directory structure of the WordPress database storage.
- Enter the login details in the cPanel
- Locate the “database” section
- Several Database Management Software will appear in the options. (You now know which one to choose). Yes, right! Select phpMyAdmin
PhpMyAdmin Related Problems That You Can Encounter
Sometimes the server rejects the connection of PhpMyAdmin because of a typo in a username or a password. Suppose you are not able to recall your credentials exactly. In that case, you can gain access to the control panel again by following the tutorial below.
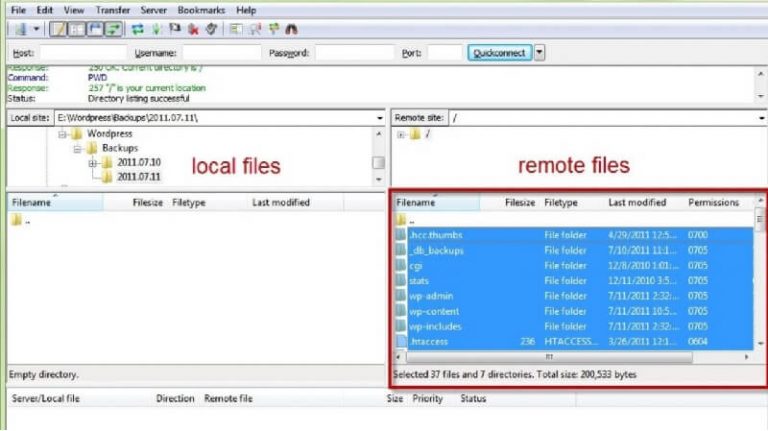
- Set up a connection with your webspace using an FTP client like a FileZilla.
- Here you will find all the files of your website in the root directory.
- Open up the wp-config.php file from the public folder. Open this file in the text editor.
-
Locate the keywords DB_USER and DB_PASSWORD and enter the correct credentials in the phpMyAdmin to access your database.
- Go to the post_type option and click it.
- Sort the content according to its nature. The post type for attachment is "" attachment." In our case, we will go for "posts" for the posts, and "pages" for the pages.
How To Apply The Search Filter On Wp_Posts?
- Go to the post_type option and click it.
- Sort the content according to its nature. The post type for attachment is "attachment." In our case, we will go for "posts" for the posts, and "pages" for the pages.
Why And How To Manually Backup Databases In Your WordPress Site?
WordPress websites have an Open-Source nature. This means hackers have an open opportunity to track security vulnerabilities and scrutinize the underlying code.
In most cases, WordPress sites are safe from potential threats. You can also enhance your WordPress website’s security by using one of the many WordPress security plugins.
But again, the open-source feature of WordPress does make it vulnerable. And then there are sudden crash downs, or what accidental loss of all your web page data? What do you do to prevent such unwanted incidents?
Unfortunately, in some cases, even a security plugin cannot be helpful. To ensure that you don’t lose your data, we suggest you manually back up the data.
In fact, you should have multiple copies of your code to restore the website painlessly without losing potential customers who need to visit your web page during the breakdown.
Even if your WordPress hosting service provides the necessary backups, follow the simple steps below to back up your website’s database:
Note: Do this by dragging all the selected WordPress database files from the right pane to the left pane.
- Open any FTP file, preferably FileZilla
- Access your account
- Save all the data in your local directory
Conclusion
While the WordPress Dashboard makes it very easy to run your website, some tasks require your manual attention.
Therefore, knowing where your database, specifically your posts and pages inside WordPress are stored will come handy when you need to edit them or troubleshoot an error. This makes it much easier for you to create and manage your WordPress site.
Your precious feedback is welcomed. How helpful did you find this guide? Share your comments and regarding the WordPress database, security, plugins, themes, or file structure in the comments section below!






